Pig kidney transplanted into living person for first time
首次將豬的腎臟移植到活人的體內
Health
There are three key advances that have finally made xenotransplantation a reality, said Dr. Joren Madsen, director of the Massachusetts General Transplant Center. First, eGenesis was able to use CRISPR-Cas9 technology to make 69 precise edits to the pig’s DNA – in some areas, snipping things out, in other spots putting things in – to prevent the human body from recognizing the pig kidneys as foreign and rejecting them. They knocked out three genes that for sugars that are expressed on the surface of pig cells that can be recognized by human antibodies and attacked. They also used gene editing to deactivate pig retroviruses that can reawaken and infect humans. The second: Pharmaceutical companies were able to make special monoclonal antibodies specifically tailored to prevent the rejection of pig organs. Finally, Madsen said, they were able to test pig organs in non-human animal models to develop the best protocols to translate the technology to people. “This successful procedure heralds a new era in medicine in which we have the potential to eliminate organ supply as a barrier to transplantation and realize our vision that no patient dies waiting for an organ,” Dr. Michael Curtis, CEO of eGenesis, said in news release.
---from CNN
麻州總醫院 General Transplant Center主任Joren Madsen博士說,有3個關鍵進展最後實現了異種移植。 首先,eGenesis 能夠使用 CRISPR-Cas9 技術對豬的DNA進行69次精準編碼——在某些地方剪掉一些東西,在其他地方插入一些東西——以防止人體將豬腎臟識別為異物而排斥它們。他們敲除了3個呈現在豬細胞表面的糖基因,這基因可以被人類抗體辨識出來並進行攻擊。他們也使用基因編碼來停止可以重新喚醒並感染人類的豬隻反轉錄病毒。 其次,製藥公司能夠製造出特殊的單株抗體,以防止豬器官的排斥反應。 最後, Madsen說,他們能夠在非人類動物模型中測試豬器官,從而開發出將此技術應用於人體的最佳方案。 eGenesis的執行長Michael Curtis博士在新聞發布會上表示:「這項成功的手術,預示著醫學的新時代,我們有可能消除將器官用於移植方面的障礙,並實現我們的願景,也就是沒有病人在等待器官的過程中死亡。」。
---摘錄翻譯自CNN
US life expectancy improved in 2022, but child deaths rose, and drug overdoses were deadlier than ever
2022年美國預期壽命有所改善,但兒童死亡率上升,且藥物過量致死率比以往任何時候都高
Health
Nearly 108,000 people died from a drug overdose in 2022, about 1,200 more than in 2021, according to another CDC report published Thursday. There are a lot of factors contributing to the overdose epidemic in the US, making it harder to shift the trend from an increase in deaths to a decrease, said Susan Sherman, a Bloomberg Professor of American Health at the Johns Hopkins University Bloomberg School of Public Health. The Covid-19 pandemic may have exacerbated some factors that were contributing to the US overdose epidemic, but it also created opportunities to better reach people with services and support, such as increased flexibility for remote prescribing of medications used to treat opioid use disorder. Some of those flexibilities have started to scale back in recent years. “There are these evidence-based interventions that really need to be scaled up in a way to reduce the burden of harm in people’s lives,” Sherman said, but they’re not equally accessible to everyone. “We know that this whole continuum of care is something that needs to be accessible to people, but they don’t have the maximum benefit when they’re not scaled up.”
---from CNN
根據CDC於週四發布的另一份報告,2022 年有近108,000人死於藥物過量,比 2021 年增加約1,200人。 約翰霍普金斯大學 Bloomberg 公共衛生學院Susan Sherman教授表示,有很多的因素導致美國藥物過量的流行,這使得死亡人數從上升轉向下降的趨勢變得更加困難。 Covid-19大流行可能加劇了導致美國藥物過量流行的一些因素,但它也創造了更好的為人們提供服務和支持的機會,例如增加用於治療鴉片類藥物使用障礙的遠距處方藥物的彈性。近年來,其中一些彈性已開始縮減。 Sherman說:「這些實證醫療介入措施確實需要擴大規模,以減輕人們生活中的傷害負擔,」但並不是每個人都能平等地獲得這些醫療介入措施。「我們知道,人們需要獲得完整且連續的照護,但如果不擴大規模,他們就無法獲得最大的好處。」
---摘錄翻譯自CNN
Nearly 5 million animals dead in Mongolia’s harshest winter in half a century, aid agencies say
援助機構稱,蒙古遭遇半世紀以來最嚴酷的冬季,近500萬隻動物死亡
Culture
Mongolia is freezing through its harshest winter in half a century with extreme conditions killing more than 4.7 million animals and threatening the livelihoods and food supply of thousands of people, the International Federation of the Red Cross has warned. The severe conditions, known as dzud, are characterized by plunging temperatures and deep snow and ice that blanket grazing areas and cut off access to food for livestock. About 300,000 people in Mongolia are traditional nomadic herders and depend on their cattle, goats and horses for food and to sell at market. “For those people who are totally dependent on their livestock to survive, they have become destitute in just a few months,” Alexander Matheou, IFRC Regional Director for Asia Pacific, told CNN Thursday. “Some of them are now no longer able to feed themselves or heat their homes.” Since November, at least 2,250 herder families have lost more than 70% of their livestock, according to the IFRC. More than 7,000 families now lack access to adequate food, it added. The dzud has affected three-quarters of the country but conditions are expected to worsen as winter continues.
---from CNN
國際紅十字會警告說,蒙古正在經歷半個世紀以來最寒冷的冬季,極端氣候導致超過470萬隻動物死亡,並威脅數千人的生計和糧食供應。 這種被稱為「dzud」的惡劣氣候的特徵是氣溫驟降、厚厚的冰雪覆蓋了放牧地區,並切斷了牲畜獲取食物的途徑。 蒙古約有30萬人是傳統的遊牧民族,他們依靠牛、山羊和馬作為食物並在市場上出售。 國際紅十字會會亞太地區的主任Alexander Matheou週四告訴CNN:「對於那些完全依賴牲畜生存的人來說,他們在短短幾個月內就變得一貧如洗。」「他們其中有些人現在已經無法養活自己或為房屋取暖。」 據國際紅十字會表示,從去年 11月以來,至少有2,250個牧民家庭失去了70%以上的牲畜。報告補充說,目前有7,000多個家庭無法獲得足夠的食物。 暴風雪已經影響全國四分之三的地區,但隨著冬季的持續,情況預計會更惡化。
---摘錄翻譯自CNN
Researchers found a tiny skull with wide eyes and a cartoonish grin. It could help solve an evolutionary puzzle
研究人員發現了一個小頭骨,它有著大大的眼睛和卡通般的笑容。它可以幫助解決演化上的難題
Culture
Paleontologists with the Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History have discovered a previously unknown prehistoric species — a 270 million-year-old amphibian with wide eyes and a cartoonish grin — and its name is a nod to an iconic froggy celebrity. Kermit the Frog meet Kermitops gratus, the most recent ancient amphibian to be identified after examination of a tiny fossilized skull that once sat unstudied in the Smithsonian fossil collection for 40 years, according to a paper published Thursday in the Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. Predating the dinosaurs, Kermitops is believed to have roamed the lower Clear Fork Formation of Texas during the Early Permian Epoch 298.9 million to 272.3 million years ago. The skull of the ancient amphibian, measuring just over an inch (about 2.5 centimeters) long, features big oval eye sockets and — due to its slightly crushed state — a lopsided smile that researchers said reminded them of the Muppet icon. The discovery of the new amphibian species could provide some answers to how frogs and salamanders evolved to get their special characteristics today, the authors wrote in the paper.
---from CNN
Smithsonian國家自然歷史博物館的古生物學家發現了一種以前不為人知的史前物種——一種2.7億年前的兩棲動物,有著大大的眼睛和卡通般的笑容——它的名字是向一位標誌性的青蛙名人致敬。 根據週四發表在《林奈學會動物學雜誌》上的一篇論文,—Kermit蛙和Kermitops gratus相遇了!在對Smithsonian博物館化石收藏品中40年來未被研究的一個微小頭骨化石進行研究後,發現了最新的古代兩棲動物。 在恐龍出現之前,Kermitops被認為在2.989億至2.723億年前的二疊紀早期就漫步於德州Clear Fork下層。這種古代兩棲動物的頭骨只有一英寸(約2.5 厘米)多長,有大大的橢圓形眼窩,並且由於輕微擠壓的狀態而呈現出不平衡的微笑,研究人員表示這讓他們想起了布偶圖示。 作者在論文中寫道,新的兩棲動物物種的發現可以為青蛙和蠑螈如何進化到今天的特殊特徵提供了一些答案。
---摘錄翻譯自CNN
Google AI could soon use a person’s cough to diagnose disease
Google人工智慧很快就能利用人的咳嗽來診斷疾病
Sciences
A team led by Google scientists has developed a machine-learning tool that can help to detect and monitor health conditions by evaluating noises such as coughing and breathing. The artificial intelligence (AI) system, trained on millions of audio clips of human sounds, might one day be used by physicians to diagnose diseases including COVID-19 and tuberculosis and to assess how well a person’s lungs are functioning. This is not the first time a research group has explored using sound as a biomarker for disease. The concept gained traction during the COVID-19 pandemic, when scientists discovered that it was possible to detect the respiratory disease through a person’s cough. What’s new about the Google system — called Health Acoustic Representations (HeAR) — is the massive data set that it was trained on, and the fact that it can be fine-tuned to perform multiple tasks. The researchers, who reported the tool earlier this month in a preprint that has not yet been peer reviewed, say it’s too early to tell whether HeAR will become a commercial product. For now, the plan is to give interested researchers access to the model so that they can use it in their own investigations. “Our goal as part of Google Research is to spur innovation in this nascent field,” says Sujay Kakarmath, a product manager at Google in New York City who worked on the project.
---from Nature
由Google科學家領導的一個團隊開發了一種機器學習工具,可以透過評估咳嗽和呼吸等噪音來幫助檢測和監測健康狀況。這種人工智慧 (AI)系統經過數百萬個人類聲音段的訓練,有一天可能會被醫生用來診斷包括COVID-19和結核病在內的疾病,並評估人的肺部功能。 這並不是研究小組第一次探索將聲音作為疾病的生物標記。這個概念在COVID-19 大流行期間受到關注,當時科學家發現可以透過人類的咳嗽來檢測呼吸道疾病。 這個名為「健康聲學表徵(HeAR)」的Google系統,其新穎之處在於它訓練時所使用的海量資料集,以及它可以進行微調,以執行多項任務。 研究人員於本月稍早在尚未經過同儕審查的預印本中報告了該工具,他們表示現在判斷 HeAR 是否會成為商業產品還言之過早。目前,該計劃是讓有興趣的研究人員接觸該模型,以便他們可以在自己的研究中使用它。「作為谷歌研究的一部分,我們的目標是刺激這個新興領域的創新,」參與該計畫的紐約Google產品經理 Sujay Kakarmath 說。
--摘錄翻譯自Nature
Cutting-edge CAR-T cancer therapy is now made in India — at one-tenth the cost
尖端的 CAR-T 癌症療法現已在印度製造——成本僅為印度製造的十分之一
Sciences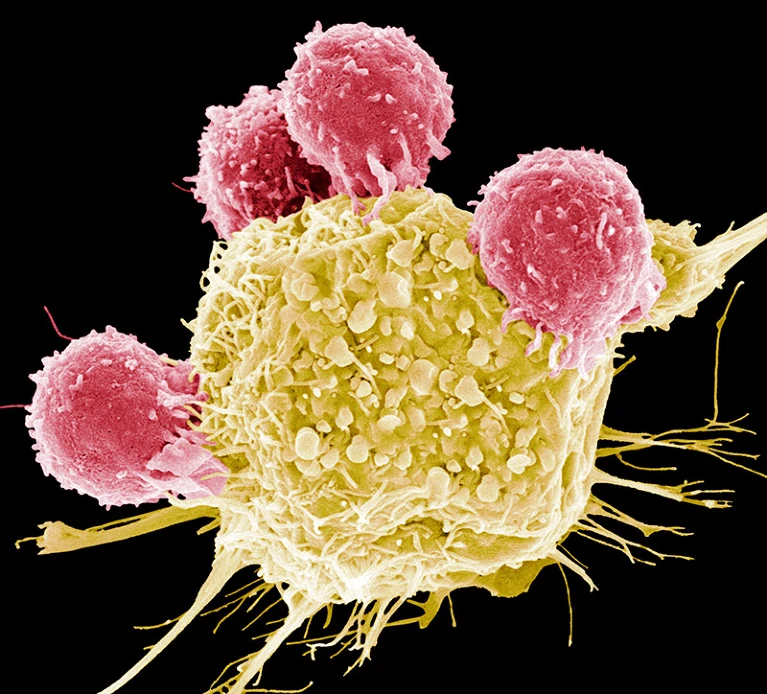
A small Indian biotechnology company is producing a home-grown version of a cutting-edge cancer treatment known as chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy that was pioneered in the United States. CAR-T therapies are used mainly to treat blood cancers and have burgeoned in the past few years. The Indian CAR-T therapy costs one-tenth that of comparable commercial products available globally. A single treatment of NexCAR19, manufactured by Mumbai-based ImmunoACT, costs between US$30,000 and $40,000. The first CAR-T therapy was approved in the United States in 2017, and commercial CAR-T therapies currently cost between $370,000 and $530,000, not including hospital fees and drugs to treat side effects. These treatments have also shown promise in treating autoimmune diseases and brain cancer. “It’s a dream come true,” says Alka Dwivedi, an immunologist who helped to develop NexCAR19 and is now at the US National Cancer Institute (NCI) in Bethesda, Maryland. Her voice becomes tender as she describes seeing the first patient’s cancer go into remission. These are people for whom all other treatments have failed, says Dwivedi. “They are getting cured.” “It’s very positive news,” says Renato Cunha, a haematologist at the Grupo Oncoclínicas in São Paulo, Brazil. He says the Indian product could pave the way for making advanced cellular therapies accessible to other low- and middle-income countries. “Hope is the word that comes to mind.” The product is also a reality check for researchers in high-income countries, says Terry Fry, an immunologist and paediatric oncologist at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus in Denver, who has advised the researchers involved in setting up ImmunoACT. “It lights a little fire under all of us to look at the cost of making CAR-T cells, even in places like the United States.”
--from Nature
印度一家小型生物技術公司正在生產一種本土版的尖端癌症治療方法,稱為嵌合抗原受體 (CAR) T 細胞療法,該療法在美國率先推出。CAR-T療法主要用於治療血癌,並在過去幾年蓬勃發展。印度 CAR-T療法的成本僅為全球同類商業產品的十分之一。 孟買的ImmunoACT公司所生產的NexCAR19單次治療費用在30,000美元至40,000美元之間。第一個CAR-T療法於2017年在美國獲得批准,目前商業化CAR-T療法的費用在37萬至53萬美元之間,這還不包含醫院費用和治療副作用的藥物。這些療法在治療自體免疫疾病和腦癌方面也顯示出希望。 協助開發NexCAR19的免疫學家AlkaDwivedi 說「夢想成真了,」,她現在在馬裡蘭州Bethesda的美國國家癌症研究所 (NCI)工作。當她描述看到第一位採用此療法而癌症得到緩解的病人時,她的聲音變得溫柔起來。Dwivedi說,對這些人來說,所有其他治療方法都失敗了。「而他們正在被治癒。」 「這是非常積極的消息,」巴西聖保羅 Grupo Oncoclínicas 的血液學家 Renato Cunha 說。他說,印度的產品可以使其他中低收入國家獲得先進的細胞療法成為可能。「我想到的就是希望這個詞。」 The University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus in Denver的免疫學家和兒科腫瘤學家Terry Fry說,該產品對高收入國家研究人員來說,也是一種對現實的檢驗。他曾經為參與建立ImmunoACT的研究人員提供建議。 「即使在美國這樣的地方,這也讓我們所有人對製造CAR-T細胞的成本產生了興趣。」
--摘錄翻譯自Nature
