WHO declares mpox outbreak a global health emergency
世界衛生組織宣布MPOX疫情為全球衛生緊急事件
Health
The World Health Organization on Wednesday declared the ongoing mpox outbreak in Africa a global health emergency. WHO convened its emergency committee amid concerns that a deadlier strain of the virus, clade Ib, had reached four previously unaffected countries in Africa. This strain had previously been contained to the Democratic Republic of Congo. The independent experts met virtually Wednesday to advise WHO Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus on the severity of the outbreak. After that consultation, he announced that he had declared a public health emergency of international concern — the highest level of alarm under international health law. “The detection and rapid spread of a new clade of mpox in eastern DRC, its detection in neighboring countries that hd not previously reported mpox and the potential for further spread within Africa and beyond is very worrying,” he said. “The emergency committee met and advised me that the situation constitutes a public health emergency of international concern. I have accepted that advice.”
---from CNN
世界衛生組織週三宣布非洲正在爆發的MPOX疫情為全球衛生緊急事件。 由於擔心一種更致命的病毒株 Ib 已傳播到四個以前未受影響的非洲國家,世界衛生組織召開了緊急委員會會議。該毒株先前已被控制在剛果民主共和國。 獨立專家們於周三通過虛擬會議向世界衛生組織總幹事Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus提供有關疫情嚴重性的建議。在那次諮詢後,他宣布已將其定為國際關注的公共衛生緊急事件——國際衛生法規定的最高警報等級。 他說:「在剛果民主共和國東部發現了一種新的MPOX分支並迅速傳播,在以前沒有報告過MPOX的鄰國中也發現了這種病毒,並且在非洲內外進一步傳播的可能性非常令人擔憂。 「緊急委員會開會並告訴我,這種情況構成國際關注的公共衛生緊急事件。我已經接受了這個建議。」
---摘錄翻譯自CNN
Alcohol’s healthy halo dims as study finds drinking may be harmful for older adults, even at low levels
研究發現飲酒可能對老年人有害,即使是低度飲酒,酒精的健康光環也黯淡了
Health
Americans, and especially those under age 35, are changing their tune on alcohol use, with a growing share endorsing the view that moderate drinking is bad for health — and a new study backs them up. According to a Gallup poll released Tuesday, almost half of Americans, 45%, say that having one or two alcoholic drinks a day is bad for a person’s health. That’s the highest percentage yet recorded by the survey, which has been conducted 10 times since 2001. Younger adults are the group most likely to say drinking is bad for health, with 65% in that camp, compared with 37% of adults ages 35 to 54 and 39% of adults 55 and older. Only 8% of adults reported that they thought moderate drinking had a positive effect on health, an all-time low. More younger adults are choosing to abstain, too, as nonalcoholic “mocktails” become widely available and people feel less social pressure to drink. A different Gallup poll published last year found that 62% of adults under 35 said they drink alcohol, down 10 percentage points from 20 years earlier. However, the survey also found a 10 percentage point increase in adults 55 and older who reported drinking, and a new study says that could be harmful for their overall health.
---from CNN
美國人,尤其是 35 歲以下的人,正在改變對飲酒的態度,越來越多的人支持適度飲酒有害健康的觀點,一項新的研究也支持了他們的觀點。 根據週二發布的蓋洛普民意調查,近一半的美國人(45%)表示,每天喝一兩杯酒精飲料對人的健康有害。這是該調查迄今記錄的最高比例,該調查自 2001 年以來已進行了 10 次。 年輕人是最有可能認為飲酒有害健康的族群,這群人中有65% 的人認為飲酒有害,而35 歲至54 歲的成年人中 有37%這樣認為,55 歲及以上的成年人中有39%。 只有 8% 的成年人表示,他們認為適量飲酒對健康有正面影響,這是歷史最低水準。 隨著不含酒精的「無酒精雞尾酒」變得越來越普遍,人們對飲酒的社會壓力也越來越小,越來越多的年輕人也選擇戒酒。去年發布的另一項蓋洛普民調發現,35 歲以下成年人中有 62% 表示他們飲酒,這一比例比 20 年前下降了 10 個百分點。 然而,調查還發現,55 歲及以上的成年人飲酒的比例增加了 10 個百分點,而一項新研究稱,這可能對他們的整體健康有害。
---摘錄翻譯自CNN
No golds for India: Why the world’s most populous country punches below its weight at the Olympics
印度未獲金牌:為何世界上人口最多的國家在奧運會上表現不佳
Culture
ndia, home to more than 1.4 billion people, is the world’s most populous country, according to the United Nations. In 2022, India surpassed Britain as the world’s fifth largest economy, and last year became one of just four countries to successfully land a spacecraft on the moon. And it’s led by an ambitious prime minister who has widespread influence on the global stage. But when it comes to the Olympics, India punches below its weight. India won just six medals in Paris, falling short of its record haul of seven at Tokyo in 2021. The United States, with less than a quarter of India’s population, topped the charts with 126 medals followed by China with 91. India ranked 71st in the medal table, below nations with much smaller populations including Georgia, Kazakhstan and North Korea. India has now won just 41 Olympic medals in total since its debut in 1900, all at the Summer Games. “There is no doubt that India has been an underperformer in the Olympics and generally in global sports,” said Ronojoy Sen, author of “Nation at Play: A History of Sport in India.” “If you look at the population to medal ratio it is probably the worst.”
---from CNN
據聯合國稱,印度擁有超過 14 億人口,是世界上人口最多的國家。 2022年,印度超越英國成為世界第五大經濟體,並在去年成為僅有的四個成功將太空船登陸月球的國家之一。它由一位雄心勃勃的總理領導,他在全球舞台上具有廣泛的影響力。 但在奧運方面,印度的表現卻不盡人意。 印度在巴黎奧運會上只贏得了六枚獎牌,低於 2021 年東京奧運會上創下的七枚獎牌紀錄。 美國人口不到印度的四分之一,以 126 面獎牌位居榜首,其次是中國,獲得 91 面獎牌。 印度在獎牌榜上排名第 71 位,低於人口少得多的國家,包括喬治亞、哈薩克和北韓。 自 1900 年首次亮相以來,印度目前僅獲得了 41 枚奧運獎牌,而且全部是在夏季奧運會上獲得的。 《運動中的國家:印度體育史》一書的作者Ronojoy Sen說:“毫無疑問,印度在奧運會和全球體育運動中表現不佳。” “如果你看一下人口與獎牌的比例,這可能是最糟糕的。”
---摘錄翻譯自CNN
Japan’s economy bounces back, supporting case for more rate hikes
日本經濟回暖,支持進一步升息
Culture
apan’s economy expanded by a much faster-than-expected annualized 3.1% in the second quarter, rebounding from a slump at the start of the year thanks to a strong rise in consumption and backing the case for another near-term interest rate hike. The Bank of Japan had forecast that a solid economic recovery will help inflation sustainably hit its 2% target, and justify raising interest rates further after it hiked them last month in its continued quest to exit years of massive monetary stimulus. The increase in gross domestic product (GDP) compared with a median market forecast for a 2.1% gain, and followed an upwardly revised 2.3% contraction in the first quarter, government data showed on Thursday. The reading translates into a quarterly rise of 0.8%, beating a 0.5% increase expected by economists in the Reuters’ poll. “The results are simply positive overall, with signs for a pick-up in private consumption backed by real wage growth,” said Kazutaka Maeda, an economist at Meiji Yasuda Research Institute.
---from CNN
日本經濟第二季年化成長3.1%,遠快於預期,得益於消費強勁成長,從年初的低迷中反彈,並支持近期再次升息。 日本央行曾預測,穩健的經濟復甦將有助於通膨持續達到2%的目標,並在上個月升息後進一步升息,以繼續尋求退出多年的大規模貨幣刺激政策。 週四政府數據顯示,國內生產毛額 (GDP) 增幅高於市場預測的2.1%增長中位數。此前,第一季度的經濟收縮數據已被上調至2.3%。 該讀數意味著季度增長 0.8%,超過了路透社調查中經濟學家預期的 0.5% 增長。 Meiji Yasuda研究所的經濟學家 Kazutaka Maeda 表示:“總體而言,結果是積極的,有跡象表明私人消費在實際工資增長的支持下有所回升。”
---摘錄翻譯自CNN
Stonehenge’s enigmatic centre stone was hauled 800 kilometres from Scotland
巨石陣神秘的中心石是從蘇格蘭 800 公里運來的
Sciences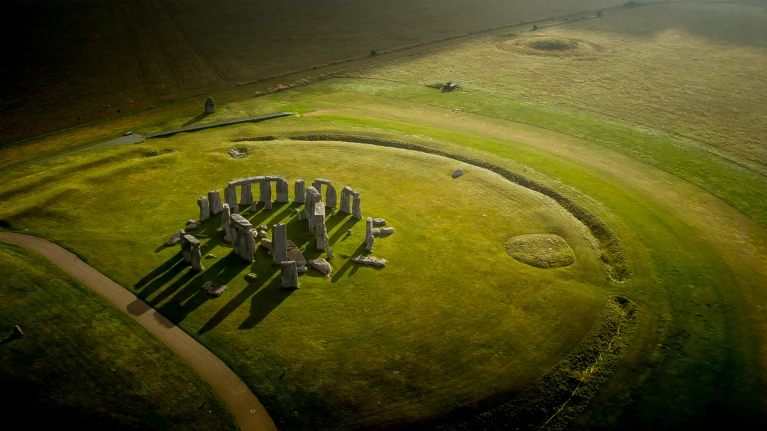
Stonehenge, the Neolithic stone circle on Salisbury Plain in southern England, has captivated archaeologists, antiquarians and sightseers for centuries. In the twelfth century, cleric Henry of Huntingdon described the haunting assemblage as one of the great wonders of England, adding that no one knew who built it or why. Over the millennia, its building has been variously attributed to the Romans, the Vikings, the Saxons, druids — and even Merlin, King Arthur’s court magician who, by one medieval telling, used his wizardly powers to whisk the stones over the seas from Ireland. A geochemical analysis of the Altar Stone, a partially buried slab of sandstone at the centre of the stone circle, now suggests the truth might be an even livelier tale. In a study published in Nature on 14 August, scientists posit that some 4,500 years ago, Neolithic mariners might have transported this six-tonne monolith more than 800 kilometres by sea from the far north of Scotland — distinguishing its origin from the other stones, which came from England and Wales. The discovery has thrilled archaeologists. “It’s a fantastic study with some big implications,” says Jim Leary, a field archaeologist at the University of York, UK. The findings increase researchers’ understanding of the henge’s builders, people of a Neolithic society that lived in Britain between about 4300 and 2000 bc.
---from Nature
巨石陣是英格蘭南部索爾茲伯里平原上的新石器時代石圈,幾個世紀以來一直吸引著考古學家、古物學家和觀光客。十二世紀,亨廷頓的牧師Henry將這個令人難忘的建築群描述為英格蘭的偉大奇蹟之一,並補充說沒有人知道是誰建造的,也不知道為什麼建造它。幾千年來,人們對它的建造有不同的看法,認為是羅馬人、維京人、撒克遜人、德魯伊特教的祭司,甚至是亞瑟王的宮廷魔術師Merlin的功勞,根據中世紀的傳說,他利用自己的魔法力量將這些石頭從愛爾蘭帶到了海上。 對祭壇石(位於石圈中心的部分埋藏的砂岩板)的地球化學分析表明,真相可能是一個更生動的故事。在8 月14 日《自然》雜誌上發表的一項研究中,科學家推測,大約4,500 年前,新石器時代的水手可能已經將這塊重達6 噸的巨石從蘇格蘭最北端經海路運輸了800 多公里,這將其來源與其他來自英格蘭和威爾士的石塊區分開來。 這項發現讓考古學家興奮不已。英國約克大學的田野考古學家Jim Leary 表示:“這是一項出色的研究,具有重大意義。”這些發現加深了研究人員對巨石陣建造者的了解,他們是生活在公元前 4300 年至 2000 年英國新石器時代的人們。
---摘錄翻譯自Nature
How a trove of cancer genomes could improve kids’ leukaemia treatment
大量癌症基因組如何改善兒童白血病的治療
Sciences
An aggressive blood cancer that mainly affects children has 15 distinct subtypes, each linked to a particular outcome and responsiveness to drugs, according to a genomic analysis. The work holds promise for improving treatment — for example, sparing some children the harshest chemotherapy regimens and giving others the latest immune therapies. This detailed classification paves the way for targeted therapies, researchers say, offering hope for people with T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (T-ALL), which comprises roughly 5% of all paediatric cancers. The work, published today in Nature, might help to predict who is less likely to respond to treatment, and it could guide doctors in selecting more-effective therapies from the start. “It’s a wonderful study that will be a very rich resource for everybody … treating T-ALL patients,” says Jan Cools, a researcher in leukaemia genetics at the Flemish Institute for Biotechnology in Ghent, Belgium
--from Nature
根據基因組分析,要影響兒童的侵襲性血癌有 15 種不同的亞型,每種亞型都與特定的結果和對藥物的反應性相關。這項工作有望改善治療——例如,讓一些兒童免於最嚴厲的化療方案,並為其他兒童提供最新的免疫療法。 研究人員表示,這種詳細的分類為標靶治療鋪平了道路,為 T 細胞急性淋巴性白血病 (T-ALL) 患者帶來了希望,T-ALL約佔所有兒童癌症的 5%。今天發表在《自然》雜誌上的這項研究可能有助於預測誰不太可能對治療產生反應,並且可以指導醫生從一開始就選擇更有效的療法。 「這是一項精彩的研究,對於治療T-ALL 患者的每個人來說都是非常豐富的資源,」比利時根特佛蘭德生物技術研究所的白血病遺傳學研究員Jan Cools 說道。
--摘錄翻譯自Nature
