Air pollution killing 1,200 young people in Europe each year
空氣污染導致歐洲每年1,200 名年輕人死亡
Health
Air pollution causes the death of more than 1,200 children and adolescents every year in Europe, according to a report released by the European Environmental Agency (EEA) on Monday. "Children are particularly vulnerable to air pollution, from when they are in the womb to when they reach adulthood," the Copenhagen-based agency said in its report. "Although the number of premature deaths in this age group is low relative to the total for the European population estimated by EEA each year, deaths early in life represent a loss of future potential and come with a significant burden of chronic illness, both in childhood and later in life," it added. Exposure to high air pollution also causes higher rates of asthma, which already afflicts 9% of children and adolescents in Europe, as well as reduced lung function, respiratory infections and allergies.
--from Deutsche Welle
根據歐洲環境署(European Environmental Agency, EEA)週一發佈的報告,空氣污染導致歐洲每年有超過1,200名兒童及青少年死亡。「兒童特別容易受到空氣污染影響,從他們在母親子宮內到成年前都是如此。」總部位於哥本哈根的該機構在報告中表示。報告補充道「儘管相較於EEA每年估計的歐洲人口總數來說,該年齡組早逝的人數較少,但過早夭折代表著未來潛力的耗損。並且這意味著他們無論是在童年還是後期生活中都將伴隨著重大的慢性疾病負擔」。暴露在高水平的空氣污染的環境還會導致更高的哮喘發病率,而歐洲已有9%的兒童及青少年患有哮喘,同時還會肺功能降低、呼吸道感染和過敏等影響。
--摘錄翻譯自Deutsche Welle
Red meat and refined carbs linked to 70% of type 2 diabetes cases globally
紅肉和精製碳水化合物與全球70%的第2型糖尿病例有關
Health
In 2018, 70.3% of the world’s 14.1 million new diagnoses of type 2 diabetes (T2D) were attributable to 11 dietary factors, according to a new study. Three dietary factors, in particular, stood out as being the greatest drivers of new cases of type 2 diabetes globally: insufficient amounts of whole grains and over-consumption of refined grains and wheat and processed meats. Of all the new cases caused by nutrition issues, a deficit in whole grains accounted for 26.1%, too many refined grains and wheat 24.6%, and processed meat intake 20.3%. Overall, poor carbohydrate quality stands out as the leading factor in the development of type 2 diabetes. Global data from 2017 found that roughly 462 million people worldwide had type 2 diabetes. It is estimated that by 2030, that number will rise to over 540 million people with the disease.
--from Medical News Today
根據一項新研究,2018年全球1410萬例新診斷的第2型糖尿病(type 2 diabetes , T2D)中,有70.3%與11種飲食因素有關。特別是這三種飲食因素為其中的最大因素:全穀物攝入量不足、精製穀物和小麥攝入過多與加工肉類攝取過量。在所有由營養問題所引起的新病例中,全穀物攝入不足佔了26.1%,攝入過多精製穀物和小麥佔24.6%,加工肉類攝取過量佔20.3%。總體而言,攝取劣質碳水化合物是第2型糖尿病增長的主要原因。2017年的全球數據發現,全球約有4.62億人患有第2型糖尿病。估計到2030年,患者人數將增加到超過5.4億人。
--摘錄翻譯自Medical News Today
Earth Day and the 'new Big 5': 11 moving photos of vanishing wildlife
世界地球日和「新 Big 5」:11 張消逝中野生動物的感人照片
Culture
In April 2020, the wildlife photographer [Graeme Green] launched a project to flip the idea of the "Big 5" of trophy hunting on its head, inviting people around the world to vote online for their five favourite animals to photograph and see in photos; the New Big 5 of wildlife photography, as decided by the public vote, are the elephant, polar bear, lion, gorilla, and tiger. The original term referred to five African animals that were considered the most desirable trophies, and the most dangerous animals to hunt: elephant, rhino, buffalo, lion, and leopard.
--節錄自BBC Culture
2020 年 4 月,野生動物攝影師 [Graeme Green] 發起了一項計劃,目的是為了顛覆「Big 5」這個詞傳統的意義,改變狩獵野生動物作為戰利品的這個想法。此計畫邀請世界各地的人們透過網路投票選出他們最喜歡在照片中看到的五種野生動物;最終人們選出大象、北極熊、獅子、大猩猩和老虎作為野生動物攝影界的新Big 5 。最初Big 5這個詞彙指的是五種非洲動物:大象、犀牛、水牛、獅子和豹。它們被認為是最令人嚮往的戰利品,也是最危險的獵物。
--節錄翻譯自BBC Culture
Why Cornwall is resurrecting its indigenous language
康沃爾正在復興其本地語言的原因
Culture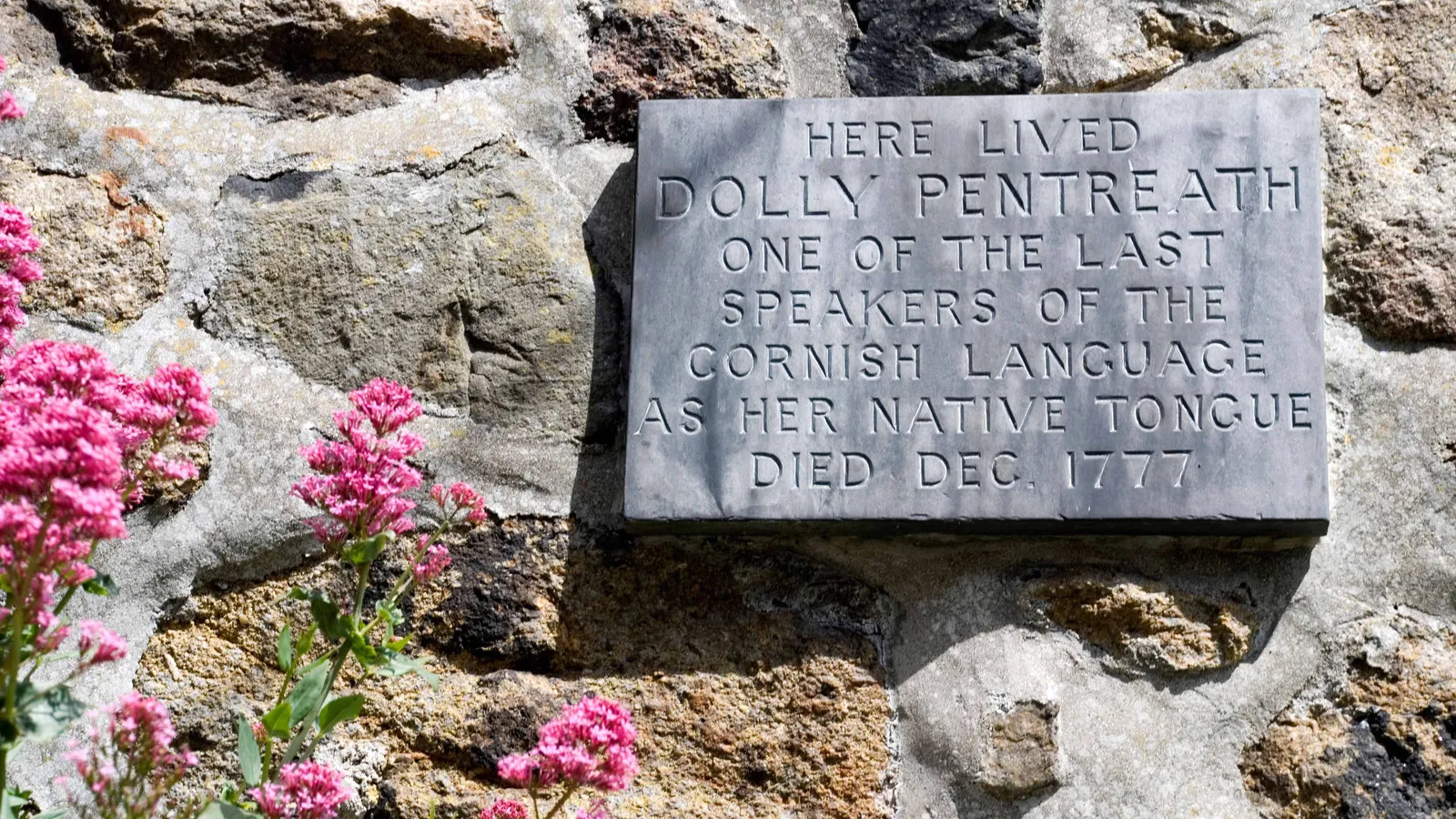
Cornwall's history, culture, and language stretch back to the end of the Roman Empire in Britain. Although modern Cornwall is one of the United Kingdom's most beloved tourist spots, the region struggles with unemployment, a housing crisis, and more, firing up calls for more independence from distant London amongst nationalist groups who are proud of their distinct heritage. A scholarly revival in the 20th Century brought Cornwall's indigenous language back from the dead, and now, as the number of speakers increases, Kernewek is helping Cornwall to cement its Celtic identity in modern Britain.
--節錄自 BBC Travel
康沃爾(Cornwall)的歷史、文化和語言可以追溯到羅馬帝國末期的不列顛島。儘管今日的康沃爾是英國最受歡迎的旅遊景點之一,但該地區卻有著高失業率、住宿危機等問題。上述問題讓當地許多以本土獨特傳統為榮的民族主義團體更加強烈的希望此區域能更獨立,與遙遠的倫敦區隔。20 世紀時的一次學術復興使康沃爾的本地語言起死回生。如今,隨著使用該語言的人數增加,Kernewek 正在幫助康沃爾鞏固其在現代英國的凱爾特(Celtic)文化身份。
--節錄翻譯自BBC Travel
First up-close images of Mars’s little-known moon Deimos
火星鮮為人知的衛星Deimos的首次特寫
Sciences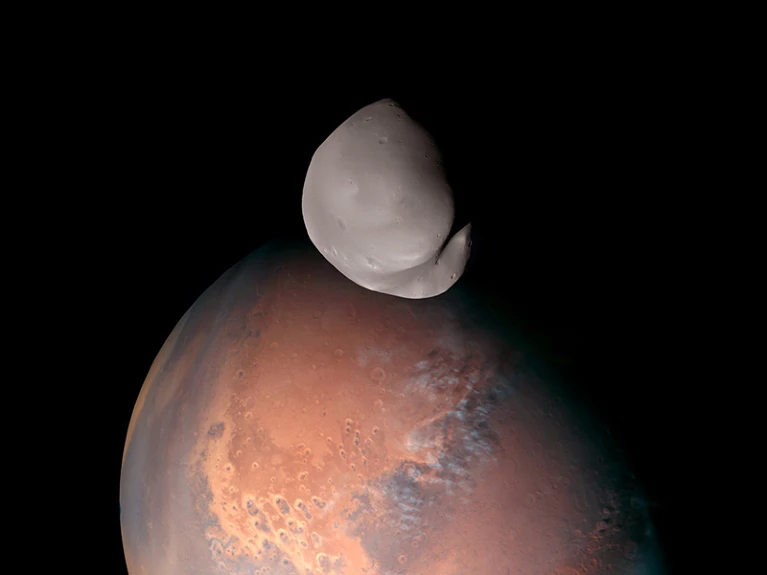
The United Arab Emirates’ space probe Hope has taken the first high-resolution images of the farside of Mars’s moonlet Deimos. The observations add weight to the theory that Deimos formed together with Mars, rather than as an asteroid that was captured in the planet’s orbit, mission scientists say. Hope, formally known as the Emirates Mars Mission (EMM), performed a fly-by — the first of many — on 10 March. “Like Earth’s Moon, Deimos is tidally locked to its planet, meaning that any observations from a low Mars orbit or the planet’s surface are always of the same side of the moonlet”, EMM science lead Hessa Al Matroushi reported the results at the European Geosciences Union meeting in Vienna on 24 April.
--from Nature news (article with video)
阿拉伯聯合大公國的太空探測器Hope拍攝了火星小衛星Deimos(戴摩斯)背面的第一批高解析度圖像。任務科學家說,觀察結果進一步證實戴摩斯與火星同時形成的理論,而非在行星軌道上被擄獲的一顆小行星。Hope正式名稱為阿聯酋火星任務(EMM),於3月10日執行了多次飛越中的首次飛越任務。EMM科學負責人Hessa Al Matroushi於4月24日在維也納舉行的歐洲地球科學聯盟會議上報告了此結果:「像地球的月球一樣,火衛二受其行星牽引鎖定,意即任何自火星低軌道或行星表面進行的觀測總是小衛星的同一面。」
--摘錄翻譯自Nature news(原文含影片)
Disease-carrying mosquitoes are spreading through Europe
病媒蚊正在歐洲擴散
Sciences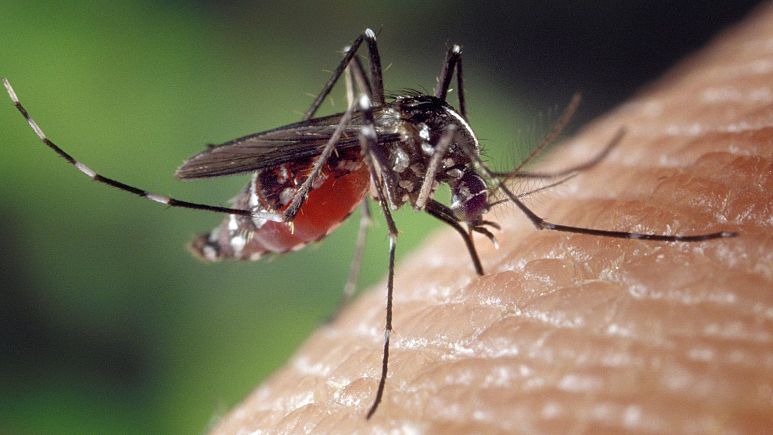
Asian tiger mosquitoes are notorious carriers of serious diseases including dengue fever, Chikungunya, West Nile and Zika. In the past 50 years, the worldwide incidence of dengue has risen 30-fold. Forty per cent of the global population, about 3 billion people, live in areas with a risk of dengue. Mosquitoes are flying northwards in the wake of global warming. Climate change means this highly invasive species is thriving across Mediterranean countries. Now researchers in the UK are embarking on a major project to assess the risk of mosquito-borne diseases in Scotland under current and future climate change scenarios. The project will also screen migratory birds to spot emerging zoonotic pathogens - diseases that jump from animals to humans - like West Nile virus.
--from Euronews
亞洲虎蚊(即白線斑蚊)是登革熱、屈公病、西尼羅病毒和茲卡病毒等嚴重疾病惡名昭彰的帶菌者。登革熱的全球發生率在過去的50年裡上升了30倍;全球40%的人口,即約30億人,生活在有登革熱風險的地區。隨著全球暖化,蚊子正向北飛行。氣候變化意味著這種高度入侵的物種正在地中海國家蓬勃發展。現在,英國的研究人員正進行一項重大計畫,以評估在當前和未來氣候變化情況下,蚊媒疾病對蘇格蘭的風險。該計畫也將篩檢候鳥,以發現新興的人畜共通病原體(由動物傳染給人類的疾病),如西尼羅病毒。
--摘錄翻譯自Euronews
